 Ranchers in West Texas frequently encounter a double-decker challenge with intense canopy coverage from honey mesquite and dense pricklypear in the understory. Synergistic broadcast herbicide applications are commonly employed to tackle these layered problematic, opportunistic, and abundant species. However, it is crucial to recognize the potential for unintended consequences on nontarget woody plant species. A recent study delved into the effects of various herbicide treatments on both target and nontarget woody plant species.
Ranchers in West Texas frequently encounter a double-decker challenge with intense canopy coverage from honey mesquite and dense pricklypear in the understory. Synergistic broadcast herbicide applications are commonly employed to tackle these layered problematic, opportunistic, and abundant species. However, it is crucial to recognize the potential for unintended consequences on nontarget woody plant species. A recent study delved into the effects of various herbicide treatments on both target and nontarget woody plant species.
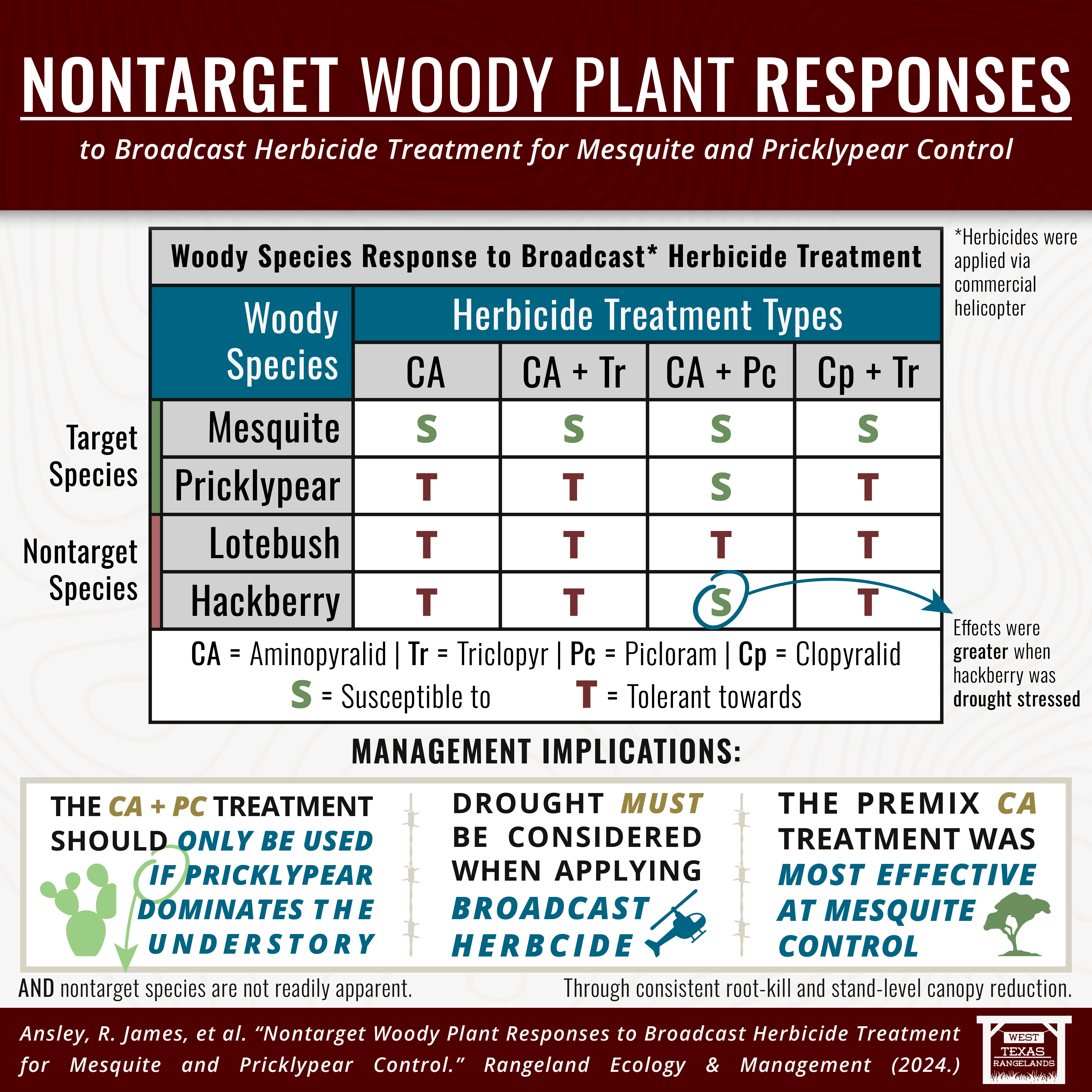
This research focused on two target species: mesquite and pricklypear and two non-target species, lotebush and hackberry.
Herbicide Treatment Combinations
The study evaluated four herbicide treatment combinations:
- CA (Aminopyralid)
- CA + Tr (Aminopyralid and Triclopyr)
- CA + Pc (Aminopyralid and Picloram)
- Cp + Tr (Clopyralid and Triclopyr)
Treatment Outcomes
Mesquite proved susceptible to all herbicide treatment combinations. Pricklypear, however, exhibited susceptibility only to the CA + Pc treatment. Lotebush demonstrated tolerance to all treatment combinations. Hackberry was susceptible to the CA + Pc treatment, particularly under drought-stressed conditions.
Management Implications
The study emphasizes several key management implications:
- The CA + Pc treatment should be employed judiciously and only when pricklypear dominates the understory, provided that nontarget species are not readily apparent.
- Drought conditions must be carefully considered when applying broadcast herbicides, as they can heighten the susceptibility of nontarget species.
- The premix CA treatment demonstrated the highest efficacy in controlling mesquite, attributed to consistent root-kill and stand-level canopy reduction.
Conclusion
This research underscores the critical importance of carefully considering the potential impacts on nontarget species when implementing herbicide treatments for woody plant control. Thorough planning and meticulous consideration of environmental factors are paramount to minimize unintended consequences and ensure the successful and sustainable management of rangeland ecosystems.
To read the full study, click Nontarget Woody Plant Responses to Broadcast Herbicide Treatment for Mesquite and Pricklypear Control
Ansley, R. James, et al. “Nontarget Woody Plant Responses to Broadcast Herbicide Treatment for Mesquite and Pricklypear Control.” Rangeland Ecology & Management (2024).