Thinking like a grassland.
What does this mean to you?
Well, to Dr. David Augustine from the USDA-ARS Station in Fort Collins, CO and others, it means large-scale movement of many species. This large-scale movement enables the Great Plains evolved strategies to contend with drought, floods, and even wildfires…in a nutshell….extreme variability in weather resulting in low forage production.
Currently, our pattern of land ownership and use of Great Plains grasslands challenges native species conservation. For example, too much management is focused at the scale of individual pastures or ranches, limiting opportunities to conserve landscape-scale processes such as fire, animal movement, and metapopulation dynamics.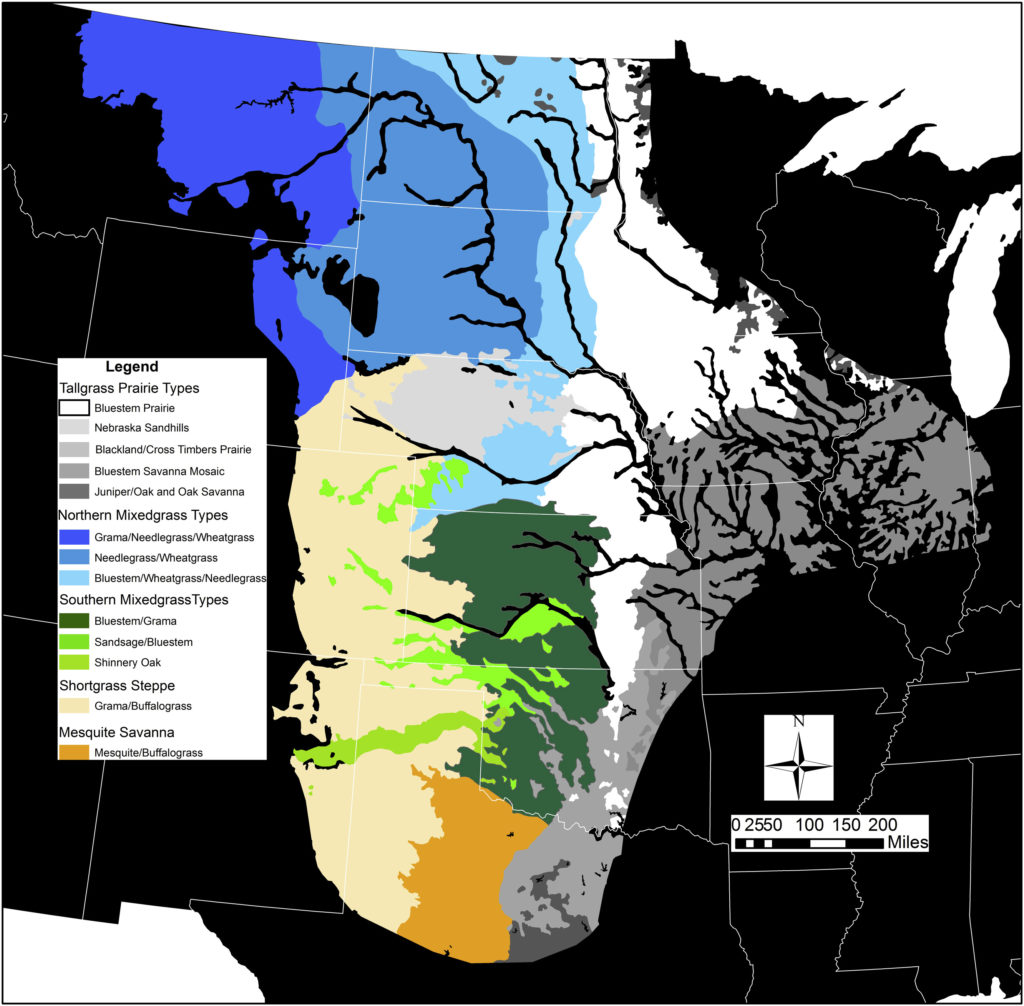
“Figure 1. Potential natural vegetation of US portion of the North American Great Plains, adapted from Kuchler (1964).”
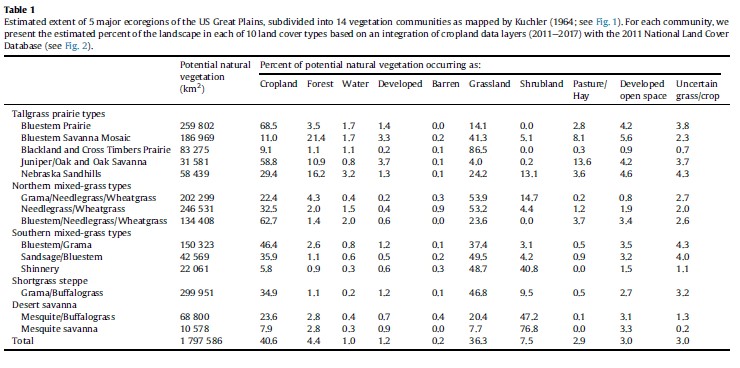
“Estimated extent of 5 major ecoregions of the US Great Plains, subdivided into 14 vegetation communities as mapped by Kuchler (1964; see Fig. 1). For each community, we present the estimated percent of the landscape in each of 10 land cover types based on an integration of cropland data layers (2011e2017) with the 2011 National Land Cover Database.”
Opportunities to increase the scale of grassland management include:
- Spatial prioritization of grassland restoration and reintroduction of grazing and fire.
- Finding creative approaches to increase the spatial scale at which fire and grazing can be applied to address watershed to landscape-scale objectives.
- Developing partnerships among government agencies, landowners, businesses, and conservation organizations that enhance cross-jurisdiction management and address biodiversity conservation in grassland landscapes, rather than pastures.
Thinking like a grassland should be pretty easy for us range managers…open spaces, big country, and…thinking big!!
For an in-depth view of “Thinking Like a Grassland: Challenges and Opportunities for
Biodiversity Conservation in the Great Plains of North America”, click on this link: Thinking like a grassland Augustine et al., 2020 REM.