Many farmers across Texas will be thinking about planting corn in just a couple of months, and sorghum shortly after that. Managing soil for good seed-soil contact and for fertilizer nutrients are common concerns as the time for planting nears, but understanding how the management of soil works into integrated pest management (IPM) programs can be helpful to ensuring the effectiveness of expensive pre-emergence (PRE) herbicide applications as well.
There are two concepts presented in this article to consider for how soils effect PRE herbicides.
1. Activity – how intense the effect of the PRE herbicide is on the target weed species
2. Persistence – length of time the herbicide remains active, or ‘persists’, in soil before breakdown proceeds to a safe level
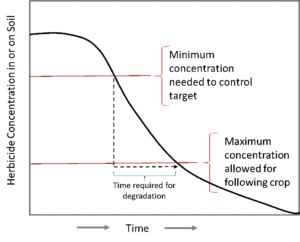
Figure 1. Pattern of herbicide persistence and degradation with time.
There are several important soil and environmental properties to be aware of when making decisions about applying PRE herbicides. Their activities, residual effect, long-term efficacy, and avoidance of tolerance development can all be affected by soil properties and soil management (Table 1). These include:
1. Soil texture (sand, silt, clay %)
2. Soil organic matter
3. Soil pH
4. Available soil water content
5. Temperature
Soil texture and organic matter (OM) affect PRE herbicide activity through interactions with soil particle surfaces and OM chemical reactivity. These interactions include adsorption (binding to particle surfaces), electrostatic interactions with OM functional groups, leaching loss below the active rooting zone, and volatilization. Soils with high percentages of clay and organic matter often protect PRE herbicides from degradation, and can even reduce their activity, through adsorptive binding. This means that the chemical may be less effective in the short term and persist longer, posing risks to subsequent crops. However, sandy soils are less likely to protect herbicides, but more likely to allow potentially volatilizable chemicals to dissipate into the atmosphere. Sandier soils also allow for rapid leaching of highly soluble chemicals. Volatilization and leaching both decrease effectiveness or activity of PRE herbicides through direct loss.
Soil pH affects PRE herbicides by limiting or hastening chemical and microbial breakdown processes (Table 1). Triazines such as atrazine, for example, will persist longer in alkaline soils (> pH 7.0). However, in acid soils, atrazine activity is decreased through adsorptive binding with clay particles, yet the compound is also degraded more quickly. Therefore, combining proper liming management of acid soils with atrazine use is a recommended practice.
As soil available water and soil temperature increase, so do PRE herbicide breakdown rates. Persistence and undesirable residual effects on subsequent crops are often observed following drought years and cooler growing seasons. Sunlight provides UV light that assists in the chemical breakdown of chemicals at the soil surface. Leaching increases with intensity and duration of rainfall events. Volatilization potential increases with temperature.
In the table below, six (6) of the most commonly applied PRE herbicides used in corn and sorghum production are discussed in terms of the soil factors that can limit or enhance activity and persistence.
Table 1. Soil factors that affect PRE herbicide activity and persistence for corn and sorghum production:
| Pre Herbicide | Soil Texture and Organic Matter | Soil pH | Soil Available Water and Temperature |
| Atrazine (AAtrex, Atrazine 4L) |
• Higher doses required to maintain activity in soils high in clays and OM | • Last• Less effective and degrade faster in acidic soils. longer in pH > 7.0
|
• UV from sunlight a minor source of loss • Persists > 1 yr in dry cold conditions |
| Saflufenacil (Sharpen) |
• Shortest persistence duration in sandy soils with good aeration | • Solubility and leaching potential increase with pH | • Does not volatilize in sandy soils |
| Dimethenamid-p (Outlook, Establish) |
• Sandier soils pose a greater risk for leaching • Medium textured (loamy) soils with < 3% OM also pose a risk for leaching |
• Not a factor | • Soluble and may leach in sandy soils following intense rainfall |
| s-Metolachlor (Brawl, Medal, others) |
• Sandier soils pose a greater risk for leaching • Medium textured (loamy) soils with < 3% OM also pose a risk for leaching |
• Not a factor | • Soluble, but less soluble than Dimethenamid-p and therefore has a lower activity |
| Acetochlor (Warrant) |
• Highly sorptive with clays and OM • Activity also increased with clay and OM content • Leaching potential increased with sand content |
• Not a factor | • Soluble and may leach in sandy soils following intense rainfall |
| Mesotrione (Callisto) |
• Short persistence duration in all textures | • Persistence longest in acidic soils | • Persistence and mobility (leaching loss potential) highest increased with cold |
If you would like to know more about soil-PRE herbicide interactions, or if you plan to use a product or chemical not covered in this article, you may find more information on this subject at EXTOXNET or at the EPA pesticides information websit online:
http://extoxnet.orst.edu/
https://www3.epa.gov/pesticides/chem_search
A large number of chemicals and the products that contain them are listed there. Find your chemical and scroll down to the “Environmental Fate” section for more information on soil and climate effects on activity and persistence. Of course, you should always read the label for every chemical you use and follow instructions for application accordingly.
Authors:
Jake Mowrer – Assistant Professor and Extension Specialist , Soil Nutrient and Water Resource Management , Texas A&M AgriLife Extension , Department of Soil and Crop Sciences
Ronnie Schnell – Associate Professor and Extension Specialist, Cropping Systems, Texas A&M AgriLife Extension, Department of Soil and Crop Sciences
Scott Nolte- Assistant Professor and State Extension Weed Specialist, Weed Science, Texas A&M AgriLife Extension, Department of Soil and Crop Sciences